Easy combining, inserting and tweaking your plugins is essential for any serious musician. In Gig Performer, plugins are connected easily using virtual wires. First, make sure that Gig Performer successfully scanned and listed your installed plugins as already advised in the Inserting and Wiring your plugins chapter.
Let's get started! Create a new empty gig and enter the Wiring view by clicking on the Wiring button:
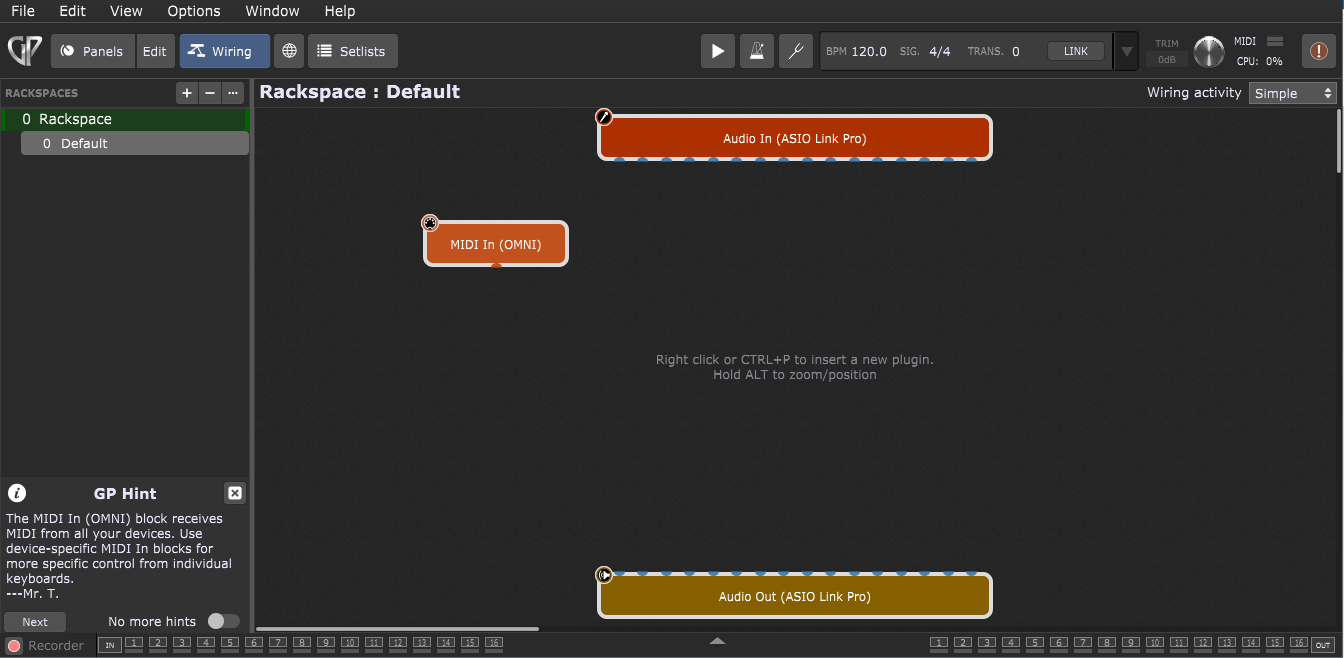
Various elements in this screenshot are explained in detail in the Wiring view chapter. Note: your screen may look slightly different from the one shown above, since the audio input and output blocks will reflect the name of your connected audio interface as well as the number of inputs and outputs it provides.
Right-click (or two-finger tap if you are using a trackpad) on the empty surface to bring up the contextual menu and select the desired plugin under the Installed plugins section, e.g. a reverb plugin:
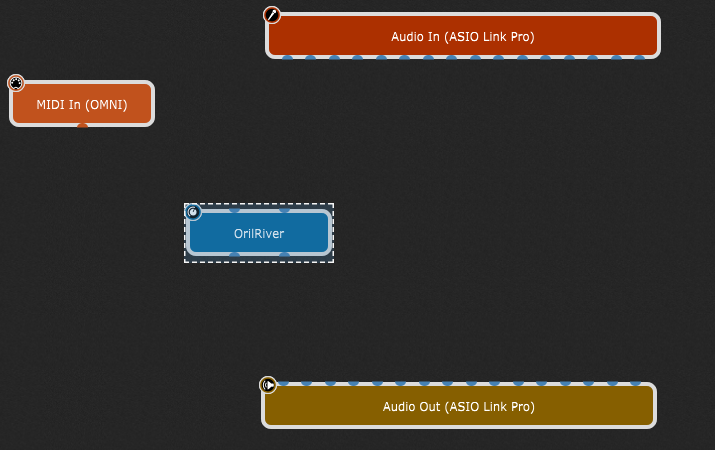
Alternatively, use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+P (or Cmd+P on Mac) to open the Quick plugin, favorite or preset finder window to search for a particular plugin by part or all of its name and insert it.
As soon as you insert the desired plugin block (or double-click on it), Gig Performer, by default opens the editor window for that plugin, allowing you to edit its parameters immediately (note: you can turn off this default behavior in the Display Options). Make the desired adjustments, or select a preset, and close the window.
Afterward, simply click on the desired plugin block and drag it to change its position on the design surface. By default, the plugin's name is displayed. Still, you can easily rename it with something that represents the actual sound, which is very useful for distinguishing among multiple copies of the same plugin. Accordingly, right-click on the newly inserted plugin block and select the Rename... option, then type in the name, i.e., "Reverb":
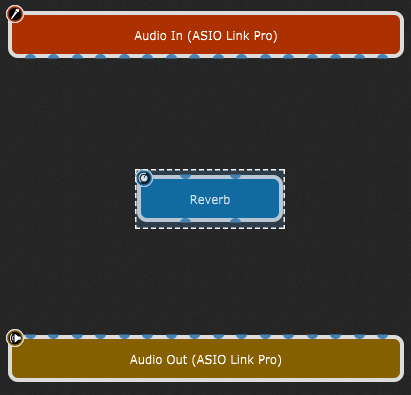
To hear the resulting sound, we need to provide an audio source. If you are a guitarist or vocalist, you might connect an Audio In pin directly to the Reverb input pin and a Reverb output pin to the Audio Out block. See the next section if you are a keyboard player using a synth plugin. To make these connections, simply click on an output pin and, while holding down the mouse button (or keeping your finger on the trackpad), drag the cursor over the desired input pin and then release the mouse button (click here for a shortcut method of making stereo connections):
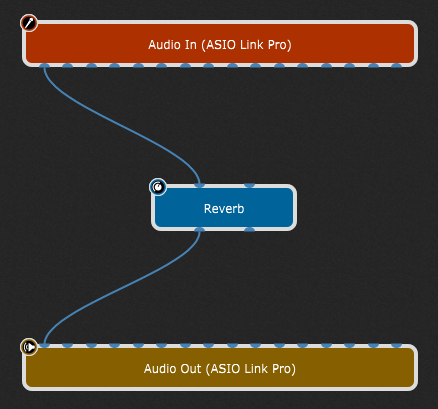
Note: make sure you connect the right Audio In pin, as your audio interface has multiple audio inputs where sources, i.e. microphones, instruments connected via DI (such as electric guitars), or other line-level sources can be connected.
Notice that there are blue and orange plugin pins and connections; click here to find out more.
If you use a MIDI keyboard or a MIDI controller, you can use it immediately thanks to the MIDI In (OMNI) block, which is available by default when creating a new empty gig (see the first screenshot). This block receives MIDI messages coming from any MIDI Input device on your system.
Note that you cannot hear the resulting sound immediately, since this block needs to be connected to the sound generating block first, and then to the Audio Out block:
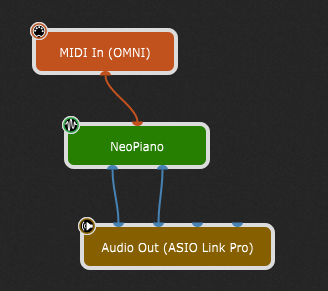
If you play a few notes on your controller (assuming your audio system is turned up), you hear a sound coming from your connected audio interface.
While the OMNI version of the MIDI In block is convenient when just getting started, if you have more than one keyboard or multiple surfaces, we recommend that you use MIDI In blocks specifically associated with those devices rather than the generic OMNI block as this will give you more control over your MIDI signal flow.
To receive MIDI messages from a specific MIDI device, right-click on the MIDI In (OMNI) block, expand Replace Plugin, and select the desired MIDI device from the MIDI Inputs list. All connected MIDI devices are listed in this menu. Alternatively, select the MIDI In (OMNI) block and press the Delete key (or the Backspace key) to remove the MIDI In (OMNI) block; afterward, open the contextual menu, insert the desired MIDI device from the MIDI Inputs list and connect its output pin to the orange input pin of your sound-generating plugin:
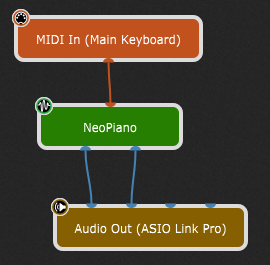
Note: if you previously created an alias for your MIDI device in the Rig Manager, it will show up in the parenthesis (otherwise, the name of the selected MIDI device will be displayed).
In addition to passing MIDI messages generated by your connected MIDI controller, MIDI In plugins provide a virtual keyboard, so you can play your plugins even if you are not using an external MIDI controller. To do so, double-click the MIDI In block to open its editor, then play the sound by clicking notes on the virtual keyboard.
To remove (disconnect) a connection, right-click on it and select "Remove this connection", or simply drag it until it detaches from a plugin and then let go.
Alternatively, hold down the Backspace key and move your mouse over the wire to remove it.
To remove all connections from a plugin block, right-click on the block and select "Disconnect" (note: removing a plugin block also removes all its connections; right-click on it and select "Remove" or press either the Delete or Backspace key).
The Wiring view features, such as zooming, scrolling, multi-selection, zoom to fit, etc. are useful while creating your plugin layout. Learn more about these features here.
Tip: to learn how to easily insert a plugin block into an audio or MIDI path, check the Additional tips chapter.