A driver is a special kind of program used to help the operating system use hardware connected to the computer. An audio driver enables Windows to recognize and interface with audio hardware.
Many audio applications support different audio driver technologies such as ASIO, DirectSound, WASAPI, WaveRT and others.
For live use you must use the ASIO drivers as they provide a low-latency and high-fidelity interface between a software application and your audio interface. They are designed with real-time audio performance in mind. Anything else will most likely not be good enough.
While Microsoft's DirectSound is commonly used as an option for non-professional users, ASIO drivers provide professional musicians and sound engineers with a faster connection to the audio hardware.
To download and install the latest ASIO drivers for your audio card or audio interface, refer to the manufacturer’s web site. We always recommend that you use the audio drivers provided by the interface manufacturer. For some audio devices however, manufacturers do not provide proprietary ASIO drivers. An example is for example the popular Behringer UMC22 where the manufacturer recommends the use of the generic ASIO4ALL driver:
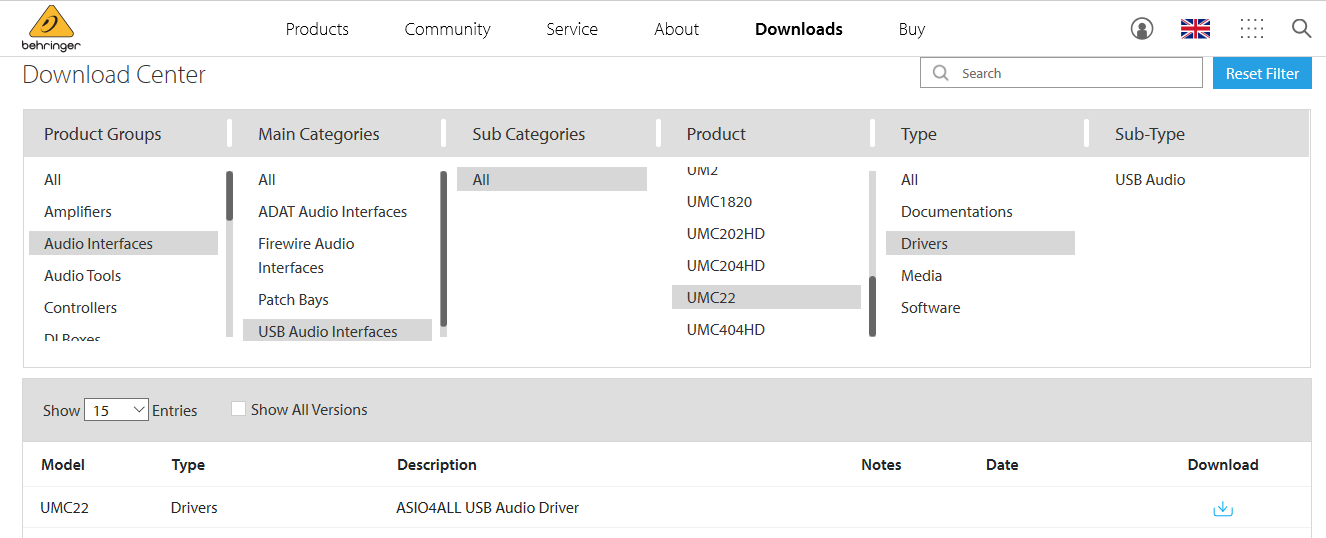
ASIO4ALL is a universal driver that acquires low level access to the sound card by using Windows kernel mode drivers and provides an ASIO interface to it.
If you have problems with your proprietary ASIO drivers, and especially if you own an older audio interface with dated ASIO drivers, such as the EMU 0404 USB you can try ASIO4ALL and see if it can improve your performance:
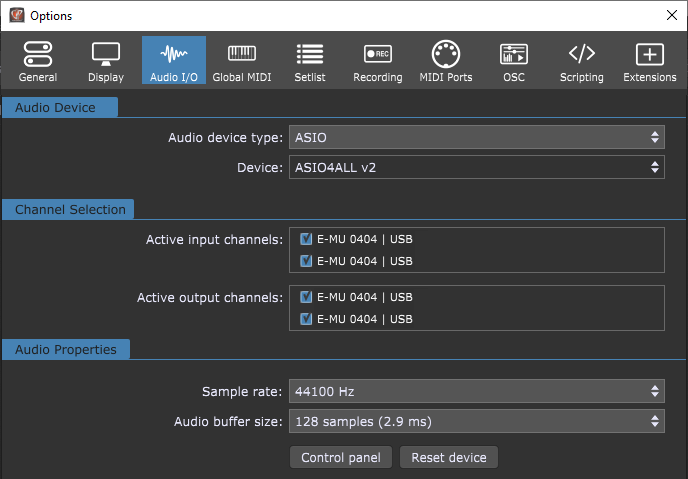
If none of these works as expected, there are a couple of other universal ASIO drivers that you might want to try, such as FlexASIO. While ASIO4ALL uses a low-level Windows audio API known as Kernel Streaming to operate, FlexASIO uses a different intermediate library called PortAudio that supports many operating system sound APIs.
If you plan to buy a new audio interface, make sure its manufacturer provides a multi-client audio driver. Unfortunately, some Windows ASIO drivers still allow only one application to use the audio interface, and these are known as single-client drivers. Multi-client audio drivers allow you to use the same audio device with more than one audio application at the same time (two instances of your audio application counts as two different applications). This is important if you plan to take advantage of Gig Performer's multi-instance feature and/or if you want to use Gig Performer together with other audio/MIDI applications.