Over time, hard drive performance can slow down due to fragmentation in the file system. When a hard drive is fragmented, its data blocks, called fragments, are scattered in multiple locations around the surface of the hard disk and so it takes longer to retrieve the required data.
Defragmentation is the process of rearranging blocks associated with individual files so that they occupy contiguous storage locations on the hard drive, to increase disk I/O performance by minimizing hard drive head travel. This reduces the time it takes to read files from and write files to the disk.
The Windows utility Defragment and Optimize Drives (formerly Disk Defragmenter) is used to defragment hard disk drives or to optimize solid state drives. Solid-state drives can also be fragmented, but that does not impact their performance as they do not have mechanical parts used for data reading and writing.
To open this utility, click on the Start button and type in Defragment; then click on Defragment and Optimize Drives app.
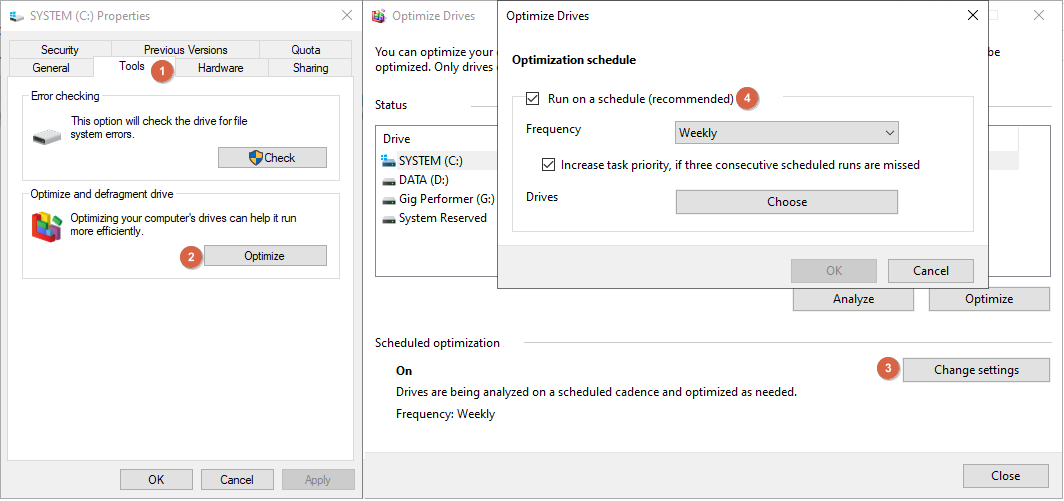
Alternatively, right click on any of your drives and select Properties. Click on the Tools tab (1), and then on the Optimize button (2). We recommend that you turn off scheduled optimization before your gig. Click on the Change settings button (3), and untick Run on a schedule option (4). You can revert this setting after your gig.
Before optimizing your hard disk drive click on the Analyze button and Windows will notify you if the drive needs to be defragmented.
When it comes to solid state drives, optimization consists of performing TRIM on an SSD drive. TRIM is a command that erases data blocks that are no longer considered in use. The use of TRIM can improve the performance of writing data to SSDs and contribute to longer SSD life.